Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become one of the most exciting and rapidly evolving fields in technology. With its ability to mimic human intelligence and perform tasks that were once thought to be exclusive to humans, AI has revolutionized various industries and sectors. This article explores the world of AI, starting with its definition and history, followed by an examination of different types of AI and ethical considerations. Here are the key takeaways:
Key Takeaways
- AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that can perform tasks without human intervention.
- The history of AI dates back to the 1950s, and it has since grown exponentially, with advancements in technology and computing power.
- AI has numerous applications across various industries, including healthcare, finance, transportation, and entertainment.
- There are different types of AI, including Narrow AI, which is designed to perform specific tasks, General AI, which can perform any intellectual task that a human can do, and Superintelligent AI, which surpasses human intelligence.
- Ethical considerations in AI include addressing bias in algorithms, ensuring privacy and security of data, and mitigating job displacement.
What is AI?
Definition of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. It involves the development of computer systems capable of performing tasks that would typically require human interaction. AI systems are designed to analyze data, make decisions, and solve problems, often with a level of accuracy that surpasses human capabilities. One example of AI technology is natural language processing, which enables machines to understand and respond to human speech. However, it is important to consider the ethical implications of AI, such as the potential for bias and the impact on privacy and security.
History of AI
AI has a rich history that dates back to the 1950s. The term Artificial Intelligence was coined by John McCarthy in 1956, marking the birth of this field. Early milestones in AI include the development of expert systems and the introduction of machine learning algorithms. Natural language processing (NLP) also emerged as a significant area of research, enabling computers to understand and interact with human language. NLP has since become a fundamental component of many AI applications, such as virtual assistants and language translation. The advancements in AI have paved the way for the development of intelligent systems that can perform complex tasks and solve problems with minimal human intervention.
Applications of AI
AI has a wide range of applications across various industries. One notable application is in the field of dental health services. AI technologies are being used to improve the accuracy and efficiency of dental diagnoses. For example, AI algorithms can analyze dental images and detect abnormalities or signs of diseases with high precision. This helps dentists in making more accurate diagnoses and providing appropriate treatments. AI-powered dental tools can also assist in planning and performing dental procedures, reducing the risk of errors and improving patient outcomes. Additionally, AI chatbots are being developed to provide virtual dental consultations, enabling patients to receive timely advice and recommendations. Overall, AI is revolutionizing the field of dental health services, enhancing the quality of care and improving patient experiences.
Types of AI
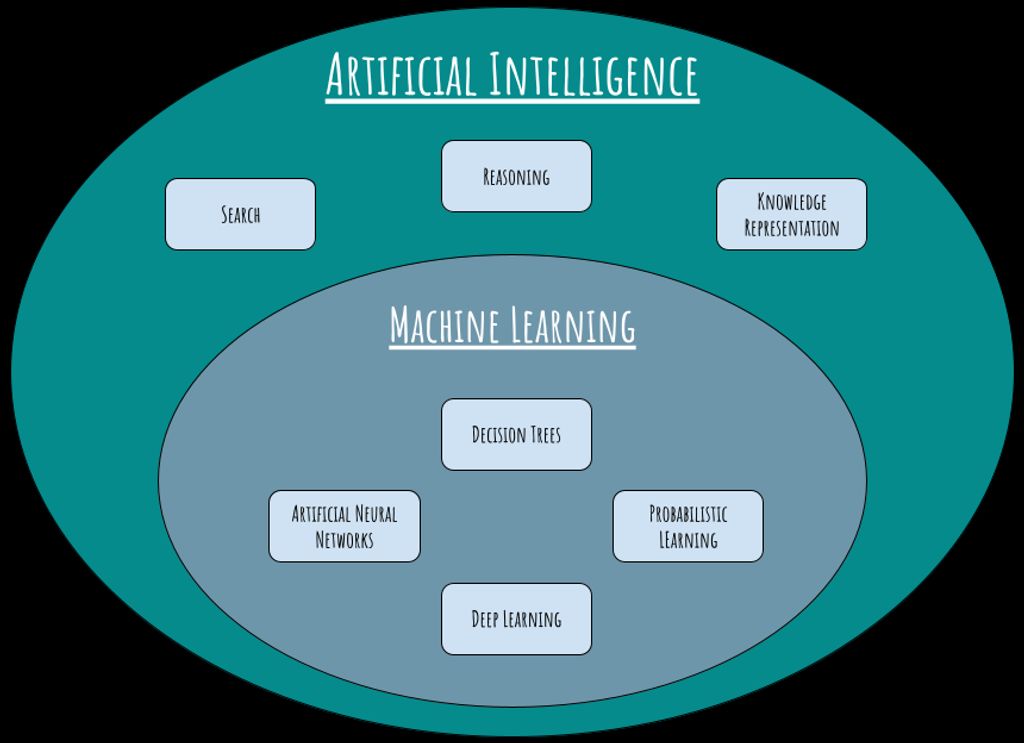
Narrow AI
Narrow AI, also known as weak AI, refers to AI systems that are designed to perform a specific task or a narrow range of tasks. These AI systems are trained to excel in a specific domain, such as image recognition or natural language processing. Unlike General AI, which possesses human-like intelligence and can understand and perform any intellectual task that a human being can do, Narrow AI is focused on solving specific problems. One example of Narrow AI is the voice assistants like Siri or Alexa, which can understand and respond to voice commands. Narrow AI has made significant advancements in various fields, including healthcare, finance, and transportation. However, it is important to note that Narrow AI is limited to the tasks it is trained for and lacks the ability to generalize or transfer knowledge to different domains.
General AI
General AI, also known as strong AI, refers to AI systems that possess the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across a wide range of tasks and domains. Unlike narrow AI, which is designed for specific tasks, general AI aims to replicate human intelligence and exhibit cognitive abilities similar to humans. The development of general AI is considered the holy grail of AI research, as it requires the creation of an AI system that can perform any intellectual task that a human being can do. Achieving general AI would have profound implications for various industries and sectors, including diamond processing. However, the realization of general AI raises important ethical considerations and challenges, such as ensuring the ethical use of AI and addressing concerns regarding job displacement and privacy and security.
Superintelligent AI
Superintelligent AI refers to AI systems that surpass human intelligence in virtually every aspect. These systems have the ability to understand, learn, and solve complex problems at an unprecedented level. They possess a wide range of cognitive abilities, including advanced reasoning, creativity, and self-awareness. However, the development of superintelligent AI raises significant ethical concerns. One of the key challenges is ensuring that these systems are aligned with human values and goals. Organizations like OpenAI are actively working on developing safe and beneficial AI systems that prioritize the well-being of humanity. It is crucial to establish robust frameworks and regulations to govern the development and deployment of superintelligent AI to prevent any unintended consequences.
Ethical Considerations in AI

Bias in AI
Bias in AI refers to the unfair and discriminatory outcomes that can result from the use of artificial intelligence systems. ChatGPT is an example of a popular AI model that has faced criticism for exhibiting biased behavior. One of the challenges in AI is ensuring that these systems are trained on diverse and representative data to mitigate bias. It is important for developers and researchers to address bias in AI to ensure fair and equitable outcomes.
Privacy and Security
In the world of AI, privacy and security are crucial considerations. As AI systems become more sophisticated and state-of-the-art, there is a growing need to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access. AI algorithms often require access to large amounts of data, which can include personal information. This raises concerns about data breaches and cyberattacks. Organizations must implement robust security measures to safeguard data and ensure the privacy of individuals. Additionally, there is a need for transparency and accountability in AI systems to address potential biases and prevent misuse of personal information. Ethical guidelines play a significant role in creating a responsible and secure AI ecosystem. It is essential to strike a balance between the benefits of AI and protecting privacy and security.
Job Displacement
As AI continues to advance, there is growing concern about the potential job displacement it may cause. AI technologies have the ability to automate tasks that were previously performed by humans, leading to a shift in the job market. While AI can increase efficiency and productivity, it also raises questions about the future of work. The fear of job displacement is not unfounded, as some studies suggest that certain industries may be more vulnerable to automation. However, it is important to note that AI also has the potential to create new job opportunities. It is crucial for society to address the ethical implications of job displacement and ensure that individuals are equipped with the skills needed to thrive in an AI-driven world.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Increased efficiency | Job displacement |
| 24/7 availability | Privacy concerns |
- AI can automate tasks and increase efficiency.
- The fear of job displacement is not unfounded.
- Certain industries may be more vulnerable to automation.
AI has the potential to create new job opportunities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is AI?
AI stands for Artificial Intelligence. It refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans.
What are the different types of AI?
There are three main types of AI: Narrow AI, General AI, and Superintelligent AI.
What is Narrow AI?
Narrow AI, also known as Weak AI, is designed to perform specific tasks and has limited capabilities outside of those tasks.
What is General AI?
General AI, also known as Strong AI, is designed to have the ability to understand, learn, and apply knowledge across different domains, similar to human intelligence.
What is Superintelligent AI?
Superintelligent AI refers to AI systems that surpass human intelligence in virtually every aspect and have the ability to outperform humans in any intellectually demanding task.
What are some ethical considerations in AI?
Some ethical considerations in AI include bias in AI algorithms, privacy and security concerns, and the potential job displacement caused by automation.

